
What comes to mind when you hear the word CBD? How about THC? Do you have positive associations with those words? Negative? Are you ambivalent? Confused?
Maybe you’re like most folks out there. You have some cursory knowledge about cannabis, but you get jumbled up when all the lingo and abbreviations come into play: CBD, THC, cannabinoid, endocannabinoid, sativa, indica. Agh, we get it — it can be confusing!
Trust us — by the end of this article, you will be a cannabis expert!
As it turns out, this confusion often leads to lots of misinformation. Hang in there, because we’re about to do some mythbusting. This article will hopefully bring you some clarity on the big questions surrounding the two main types of cannabis you’re most likely to encounter: CBD and THC.
Both CBD and THC contain some amazing properties that have the potential to dramatically change the way we treat chronic pain, anxiety, major diseases, and more. But they are quite different. Buckle up, folks, things are about to get nerdy. Trust us — by the end of this article, you will be a cannabis expert!
Properties of CBD and THC

It all starts with the cannabis plant. “Cannabis” is an umbrella term for a genus of flowering plants (remember that hierarchy from Biology 101?). Cannabis originated in Central Asia, however today it is grown all over the world. There are three species within the cannabis genus:
- Cannabis sativa
- Cannabis indica
- Cannabis ruderalis
We’ll learn more about those three species later. For now, the important takeaway is that cannabis is a natural substance that comes from the earth. Within the cannabis plant, there are over 100 different kinds of cannabinoids, which are naturally occurring chemical compounds within the plant.
Although they originate from the same plant (cannabis), CBD and THC take on very different properties.
Cannabinoids are the main agent in the healing and hallucinogenic properties in cannabis. Most of that has to do with cannabinoid’s interaction with the endocannabinoid system. Among those 100+ known cannabinoids, the most popular ones are cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
Although they originate from the same plant (cannabis), CBD and THC take on very different properties. In fact, they are separated into two entirely different cannabis strains — hemp and marijuana! Here’s the gist of it:
- CBD is the dominant cannabinoid in hemp and is non-psychoactive
- THC is the dominant cannabinoid in marijuana and is psychoactive
Hemp vs. marijuana

So what’s the difference between hemp and marijuana? Great question! Both hemp and marijuana are technically cannabis. In fact, they look almost identical to the untrained eye. But hemp contains mostly CBD (with some THC) and marijuana contains mostly THC (with some CBD). But let’s take a closer look at the chemical properties of these cannabinoids.
CBD and THC (and therefore hemp and marijuana) have virtually opposite effects on the body.
As it turns out, THC and CBD are identical in their chemical makeup. They share 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms. Based on that information, you would assume that hemp and marijuana are also identical in their medicinal and functional properties, right? Wrong. Nature is wild, folks.
Despite their identical chemical makeup, CBD and THC (and therefore hemp and marijuana) have virtually opposite effects on the body. Their identical atoms are arranged in non-identical ways (see image below).
When it comes down to it, the signifiers of hemp and marijuana are somewhat misleading in their actual classifications. It’s a bit of a stretch to even name them as strains of cannabis — their titles were decided more by societal signifiers than any formal scientific process.

Remember the three main species within the cannabis genus? Here’s a refresher:
- Cannabis sativa
- Cannabis indica
- Cannabis ruderalis
You’ve probably seen these phrases thrown around in your reading or among your cannabis-enthusiast friends (we all have them). Technically, this is a more accurate way to conceptualize the different strains of cannabis because they are distinguished based on species rather than characteristic. Here’s a quick profile on each:
- Cannabis sativa: Contains energizing, positive, and invigorating qualities. Tends to be lower in CBD and higher in THC. Often used to treat depression and anxiety, but depending on the strain, it can induce paranoia.
- Cannabis indica: Contains deeply relaxing qualities. Tends to be higher in CBD and lower in THC. Often used to treat insomnia, pain, nausea, and anxiety. Does not give as much of a cerebral high as a sativa.
- Cannabis ruderalis: Lesser-known strain. Tends to be higher in CBD and lower in THC content. Not particularly potent, so not super common or popular.
You can profile your cannabis through species descriptions (sativa, indica, ruderalis) or through their characteristics (hemp and marijuana).
Semantics and technicalities aside, hemp and marijuana are chiefly distinguished from each other because of their differing levels of THC and CBD. Hemp is any strain of cannabis that contains less than 0.3% THC. Marijuana, then, is anything that contains more than 0.3% THC. As such, marijuana contains psychoactive qualities while hemp does not.
Cannabinoids and the Endocannabinoid System
Most people don’t realize that our bodies contain an entire system that is literally set up to interact with cannabis. Crazy, right? Cannabis and cannabinoids are a natural substance. In fact, the human body evolved over 500 million years ago to incorporate it! All of that is thanks to this little-known body system.
Welcome to the endocannabinoid system, or ECS. The ECS is a relatively “new” body system, only discovered by researchers in 1988. It is sometimes referred to as the “bridge between the mind and body” because of its nuanced control of both psychological and physiological functions.
Most people don’t realize that our bodies contain an entire system that is literally set up to interact with cannabis.
The more you understand how the ECS facilitates responses to CBD and THC in your body, the more you will understand the differences and similarities of the two cannabinoids.
What is the endocannabinoid system?
Unlike the digestive system or urinary system, the endocannabinoid system is not centralized. Rather, the ECS is dispersed all throughout your body — in your skin cells, bone marrow, muscles, liver, and beyond.

Researchers are constantly discovering more places in the body where the endocannabinoid system is present. However, the ECS is most prevalent in our central and peripheral nervous system (the brain and spine).
One of the chief concerns and tasks of the endocannabinoid system is to keep your body at homeostasis: the drive toward a “steady equilibrium,” or a way of keeping the body balanced. Our bodies’ natural desire is to keep all systems balanced, meaning the ECS plays a role in some of the most vital fluctuating functions of the body:
- Sleep
- Appetite
- Mood
- Pain
- Memory
- Fertility
- Stress
- Inflammation

That’s just the tip of the iceberg; the ECS has a lot on its plate. Before we get into the nitty-gritty of the ECS, let’s introduce you to the main players in this game. Here are the three core components of the endocannabinoid system:
- Endocannabinoids
- Cannabinoid receptors
- Enzymes
Easy enough, right? First, the endocannabinoids are naturally produced molecules in your body. Maybe the name gives it away, but they actually resemble the cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant (or rather, the cannabinoids resemble the endocannabinoids)! Bottom line: We already produce cannabis-like compounds in our bodies without the help of the plant.
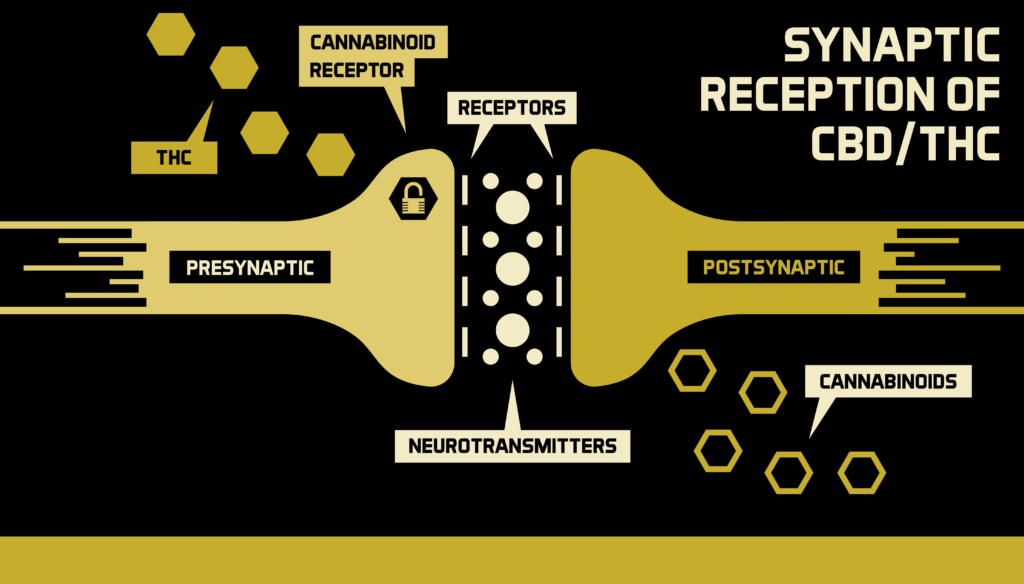
The cannabinoid receptors are spread out all over our bodies (skin, muscles, bone — you name it). These receptors receive the endocannabinoid molecules in order to carry out the intended task. Think of it as a lock-and-key type of relationship.
When your body senses a lack of homeostasis — whether that is an inflamed joint or lack of nutrients — the ECS alarm starts wailing (metaphorically speaking). It will send out a flood of endocannabinoids (those cannabis-like molecules) to find the distressed area.
The endocannabinoids travel to their respective cannabinoid receptors, link up, and together send out neurotransmitters to address the distressed area. And voilà! The siren turns off. Homeostasis is achieved: Level unlocked!
We already produce cannabis-like compounds in our bodies without the help of the plant.
Last but not least, your body calls in the enzymes, which act as a sort of clean-up crew. We don’t want the body to over-correct the imbalance, so once homeostasis is achieved, a crew of enzymes comes through and breaks up the endocannabinoid/receptor bond.
So that’s the short version of the entire process. But like most things related to the body, the science is way more complicated. When it comes to distinguishing the core differences between THC and CBD, it’s important to take a deeper look at those cannabinoid receptors: Their names are CB1 and CB2.
CB1 and CB2 receptors

Here is where things get interesting. We’ve established that endocannabinoids closely resemble the cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. We’ve also established that the ECS performs this balancing act of homeostasis constantly, without the help of the cannabis plant.
But what happens when we throw CBD and THC (known cannabinoids) into the mix? When we ingest CBD and THC, the cannabinoids take on the role of the endocannabinoid. They go searching for a cannabinoid receptor. Two in particular: CB1 and CB2.
As we mentioned before, the endocannabinoid system is a relatively new discovery. Researchers discovered the first cannabinoid receptor in 1988. Five years later, in 1993, they identified a second receptor, and in 1995, the two receptors were officially classified as the CB1 and CB2 receptors.
While both receptors act as a loading dock for cannabinoids and endocannabinoids, they facilitate very different functions.
CB1
The CB1 receptors are mostly located in our central nervous system (our brain and spinal cord). Since the receptors are mostly grouped in our “control center,” the main functions of CB1 receptors have to do with human behavior and cognitive function.
They are associated with emotion, appetite, memory, and our perception of pain. The CB1 receptors are at the hub of our reward system, which is housed in the amygdala in the brain.
Researchers have discovered that CB1 receptors are active in neuroprotective responses of the brain. This means THC could be a huge help in degenerative diseases like Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, and Alzheimer’s.
Since the receptors are mostly grouped in our “control center,” the main functions of CB1 receptors have to do with human behavior and cognitive function.
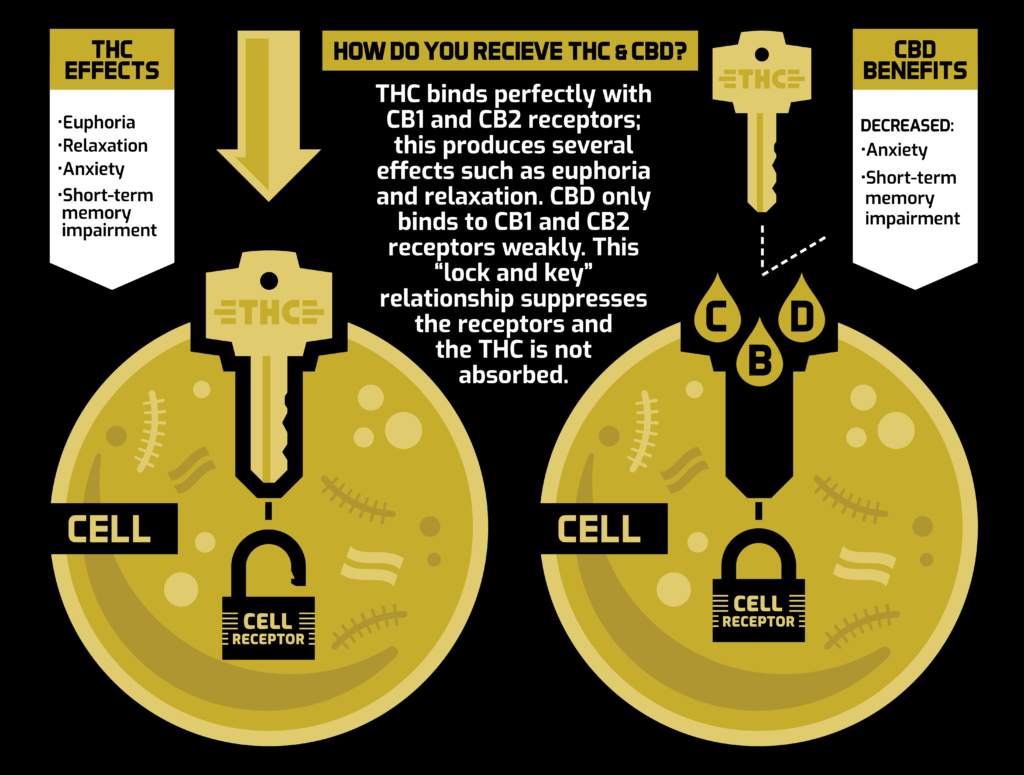
THC molecules bind perfectly with the CB1 receptors, which makes sense if you think about it: THC is a cannabinoid that has psychoactive effects. On one hand, THC can cause feelings of euphoria; on the other hand, it can result in cognitive impairment. Both effects are a result of THC binding with CB1 receptors.
CB2
CB2 receptors are found elsewhere in the body, mostly in the peripheral nervous system (which extends out to our limbs). CB2 receptors are linked to our immune system and muscular system. Researchers continue to discover connections between the CB2 receptors and the body’s response to pain and inflammation.
Rather than a cognitive response (of either euphoria or impairment), the interaction of THC and CB2 receptors yields an anti-inflammatory and pain relief response.
Interaction of CBD with CB1 and CB2 receptors
You may have noticed that we haven’t talked at all about CBD’s interaction with the cannabinoid receptors. That’s because CBD doesn’t follow the same binding patterns as THC. Whereas THC binds perfectly with CB1, CBD doesn’t bind to it at all. As for the CB2 receptor, CBD only weakly binds to it.
Instead of the lock-and-key relationship, CBD is hard at work in other ways. Let’s take a quick step back. The overall purpose of our naturally produced endocannabinoids is to maintain balance and health in the body. Over time, our bodies simply start to slowly break down, making it more difficult to reach homeostasis.
Enter CBD, a natural compound, but one we don’t produce on our own. Sometimes your body just needs a little boost. Instead of binding directly to the receptor, CBD alters it. In essence, CBD elevates the functionality of the receptors and allows the endocannabinoid system to do its intended job.

CBD does a few other cool side jobs. For one, it activates another set of receptors (TRPV1 receptors) that take care of pain perception, body temperature, and inflammation. As a result, CBD can relieve pain and act as an anti-inflammatory.
CBD also increases our natural levels of anandamide — a neurotransmitter known as the “bliss molecule” — by slowing down the enzyme that breaks up anandamide. So while CBD does not provide the same kind of euphoria that THC provides, it helps our bodies produce more natural mood enhancers.
CBD elevates the functionality of the receptors and allows the endocannabinoid system to do its intended job.
Finally, CBD also functions as an inhibitor to the psychoactive effects of THC. CBD binds very weakly to CB1, which in turn limits the ability of THC to bind to the receptor. As a result, the psychoactive effect of THC is also dampened (see image below).
Psychoactive differences between THC and CBD
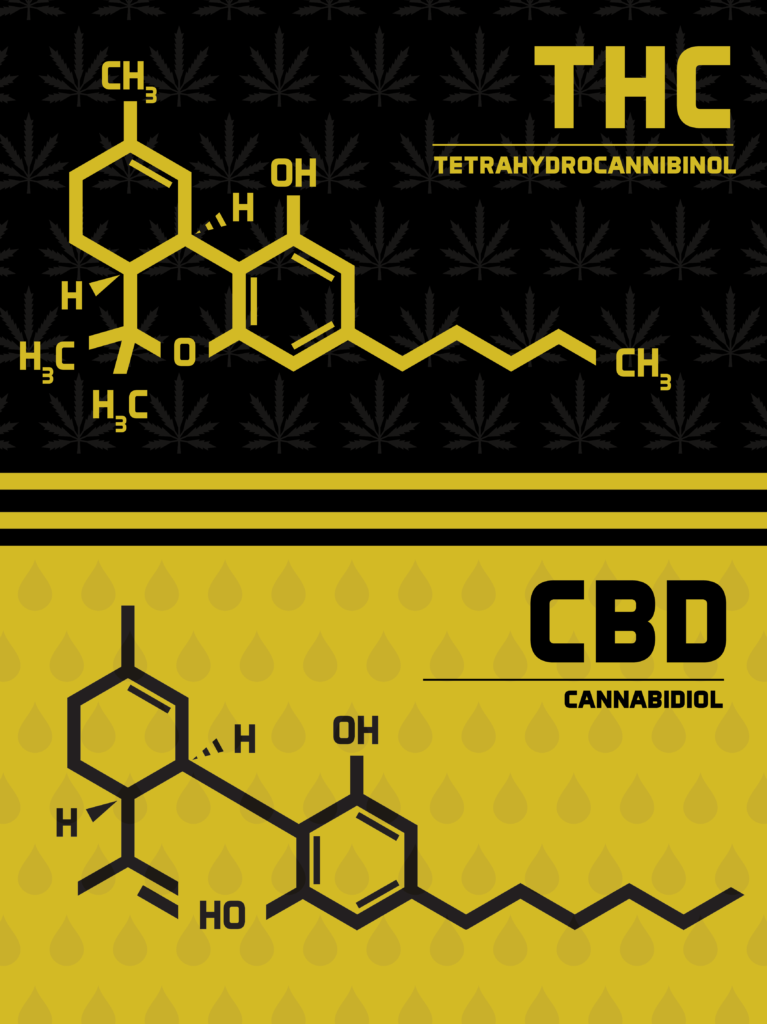
One of the most notable differences between THC and CBD is the fact that THC will get you high and CBD will not. We alluded to the reasoning behind this difference, but let’s dive a bit deeper.
It all comes down to the CB1 receptors, which are centrally located in our brains (among other places). Remember that THC binds perfectly with CB1, whereas CBD does not at all. In fact, CBD inhibits it. This means that CB1 functions can be traced exclusively to THC.
Humans have interacted with CBD and THC for many millennia.
During THC activation, brain imaging has indicated an increased blood flow to the prefrontal cortex of the brain. This part of the brain controls decision-making skills, attention, motor skills, and more. In short, it makes us high!

THC also activates the CB1 receptors in the reward center of your brain, which ignites feelings of euphoria, relaxation, pleasure, and hunger when you have THC in your system.
CBD, on the other hand, inhibits the work of the CB1 receptors. When CBD and THC are consumed together, it is typical for the psychoactive components of THC to be weakened. CBD can also decrease the paranoid feelings that sometimes accompany THC.
One of the most notable differences between THC and CBD is the fact that THC will get you high and CBD will not.
At times, THC intoxication has been branded as a threat to society. After all, marijuana is still classified as a criminalized drug at the federal level. Indeed, impaired motor and decision-making skills can sometimes yield dangerous results. However, THC can also facilitate massive healing benefits.
We’ll learn more about the multitude of medical benefits associated with CBD and THC below.
Medical Benefits of CBD and THC

Humans have interacted with CBD and THC for many millennia. As our understanding of the cannabis plant deepens, so does our understanding of the many benefits it offers. Some have dubbed cannabis a “miracle drug” for its widespread medical benefits. Even more, these benefits are accompanied by very few side effects.
The chart below offers a helpful introduction to just a few of the many health benefits that CBD and THC provide. You’ll see that the two cannabinoids share some benefits, while other benefits are specific to just CBD (like reducing seizures) or just THC (like increasing a low appetite).
| Medical Benefit | CBD | THC |
| Pain Relief | Yes | Yes |
| Reduction of Nausea | Yes | Yes |
| Headache Relief | Yes | Yes |
| Anxiety Reduction | Yes | Yes |
| Alleviates Depression | Yes | No |
| Decreases of Eliminates Seizures | Yes | No |
| Reduces inflammation | Yes | Yes |
| Relieves Insomnia | Yes | Yes |
| Helps with MS symptoms | Yes | Yes |
| Helps with IBS symptoms | Yes | Yes |
| Helps with Parkinson’s disease tremors | No | Yes |
| Helps with Psychosis | Yes | No |
| Increases Appetite | No | Yes |
Note: The benefits in the above chart are speculative. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This chart is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
While anecdotally CBD and THC are proven powerful and safe medicinal aids, cannabis has not garnered the same federal support as modern pharmaceuticals. Without federal regulation, it lacks crucial funding for scientific studies. In this case, the science lags far behind the public’s enthusiastic acceptance of CBD and THC.
Epidiolex

The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved one CBD-based drug. Epidiolex is a treatment for several severe forms of rare childhood epilepsy: Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and Dravet syndrome. Officially released in June 2018, Epidiolex is the first of its kind.
The FDA is quick to point out that Epidiolex does not contain any THC and conducted numerous controlled clinical trials before approving the drug. Epidiolex has already proven to be an effective medication for young kids. The side effects are minimal, and mostly have to do with disrupted sleep.
Side Effects of CBD and THC
As with any substance we introduce to our bodies, there is the possibility of adverse side effects. It is no different with CBD and THC. While proven to be extremely safe, they also come with a few side effects that are important to know before incorporating hemp or marijuana into your daily routine.
Keep in mind: You cannot overdose on either THC or CBD. Full stop. That said, there is such a thing as a “bad high” or consuming too much of a good thing. Our bodies all react differently. But if you are careful with your dosages of THC and CBD, you will be just fine. Just to be safe, here’s a quick look at a few negative side effects:
THC

- Difficulty concentrating
- Dizziness
- Delayed coordination
- Vomiting
- Drowsiness
- Dry mouth
- Faulty memory
- Nausea
CBD

- Diarrhea
- Upset stomach
- Lightheadedness/drowsiness
- Crankiness
- Low blood pressure


Additional precautions with CBD
Before you start using CBD regularly, it is a good idea to check in with your doctor. They will be able to advise you on dosage. But they will also help educate you on how your current medications might interact with the CBD. Strangely, some medications can mix poorly with CBD.
As a general rule, make sure your doctor signs off on your CBD usage.
Have you ever heard of the grapefruit rule? Trust us, it’s related to CBD! Basically, doctors warn against mixing certain medications with grapefruit juice. Such medications include Lipitor (a cholesterol medication) and Claritin (an allergy medication), but the list is long. Grapefruit juice interferes with certain enzymes in your liver, which in turn affects how you metabolize the medication.
If you are on any of these medications, it can be dangerous to add CBD to the mix. CBD acts in a similar way to grapefruit juice by inhibiting the enzymes that metabolize your medication. As a result, your medication is at risk of staying in your system longer. As a general rule, make sure your doctor signs off on your CBD usage.
Additional precautions with THC

In the last decade, researchers have started to see a correlation between excessive THC use among young people and schizophrenia in adulthood. This is a legitimate and concerning development, especially as marijuana use continues to be easier to access among young adults.
In a recent study at King’s College London, a professor of psychiatry found that “high-potency cannabis — approximately 16% THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) — was involved in 24% of all cases of a first episode of psychosis.”
While this is certainly cause for concern, there are some caveats. One thing to keep in mind is that so far the link between the two is just an association rather than a causation. Another counterpoint is that researchers have not seen a proportionate increase in diagnoses of schizophrenia even with the steady increase of cannabis use among the public.
Further reading: If you’re interested in reading more about why schizophrenia and high-potency THC are linked, check out these articles from Harvard Health Blog and Scientific American.
Medical Research on CBD and THC

Despite the funding limitations that significantly delay medical research on cannabis, legitimate studies have slowly started to emerge. Millions of people have already reaped the medical benefits of cannabis, but only when the medical community acknowledges cannabis through peer-reviewed research will it be fully accepted.
It might seem like CBD and THC get credited for a huge range of medical benefits. For some, their wide-reaching healing abilities seem far-fetched. It’s good to be skeptical! But allow us to also follow up those claims with some actual evidence.
- CBD use for refractory epilepsy: This 2017 study tackled refractory epilepsy, or seizures that are resistant to medication. They surveyed 15 patients who struggle with recurrent seizures, and provided CBD as medication. The frequency of seizures disappeared completely in 27% of patients, and dropped significantly for 40% of patients. All patients reported an improvement in general mood and well-being.
- THC use for HIV-associated pain: This 2007 study examined the use of smoked THC-based cannabis among patients with HIV-associated neuropathy in a randomized placebo-controlled trial. It revealed that the cannabis significantly relieved chronic neuropathy pain.
- THC use for spasticity in MS patients: In 2012, Canadian researchers studied the use of cannabis (THC-dominant) for treating spasticity in patients with multiple sclerosis. Spasticity is the continuous contraction of certain muscles. This study was a placebo-controlled trial. It found that the smoked cannabis proved a superior pain reliever and symptom-reducer than the placebo.
- CBD use for reducing generalized fear symptoms: In 2017, a group of researchers in Brazil published a study on the ways in which CBD can disrupt generalized fear responses. Using rats as their subjects, researchers found that a dose of CBD successfully activated the anandamide-mediated response in CB1 receptors, allowing the rats to jump out of the fear response faster than the control group. This study has amazing implications for PTSD-related symptoms.

- CBD preventing high blood pressure: Using a double-blind, placebo-controlled method, this 2017 study tracked CBD’s effect on high blood pressure. It found that CBD decreased the resting blood pressure of its studied patients, mostly to its calming effect on the body’s stress response.
- CBD use in reducing opioid dependence: This massive 2017 study surveyed close to 3,000 cannabis users, hoping to determine if CBD was an effective substitute for opioid-based medications. An overwhelming 97% of users self-reported that CBD use decreased their dependence on opiates. This study has serious implications for future pain management.
- CBD improving symptoms related to IBS: In 2012, researchers conducted a 3-month-long trial to determine if CBD could effectively treat symptoms related to inflammatory bowel disease (IBS). It found that regular CBD use promoted weight gain, increased BMI, and improved general quality of life measurements among the patients.
Delivery Methods of CBD and THC

The many possible delivery methods of CBD and THC make them super marketable to lots of different populations. Forget all assumptions you might have that hemp and marijuana are only consumable via “joints.” While that is a possibility, there are way more options available to you. For instance, you could try gummies, drops, capsules, topicals, and more.
The three most popular methods of taking in CBD and THC are orally, topically, or inhaling through vaping. Anatomically speaking, that means you can take CBD and THC through your mouth, skin, or lungs. We’ll take a brief look at each of the following below.
Mouth (sublingual or edibles)
One popular way of experiencing the benefits of CBD or THC is through taking their oils in numerous ways. A highly effective way is via the sublingual method. The word sublingual literally means “placed under the tongue,” so sublingual method is placing drops of CBD or THC oil under your tongue.
Why the tongue? Well, you have a ton of capillary-rich blood vessels under your tongue, which means it’s a prime spot to deliver any substance directly to your bloodstream. It is recommended to hold the oil under your tongue for 60 to 90 seconds before swallowing. You should feel the effects within the hour.

Another huge benefit of the sublingual method is that it avoids the “first-pass effect.” When we consume CBD or THC orally, it travels through our digestive system and eventually makes its way to our intestines. There, the cannabinoids are absorbed into our bloodstream and pass through the liver (via the hepatic portal system, as a matter of fact).
Among other things, the liver’s job is to filter our blood and metabolize drugs. This is the first-pass effect. Unfortunately, that means the liver sends enzymes to break down the CBD and THC molecules, dramatically reducing their potency. In fact, most of the CBD and THC ends up in your urine.
But since the sublingual method sends the CBD/THC directly to your bloodstream, you’ll bypass the first-pass effect and instead feel the entire potency of your dosage.
Pros of sublingual delivery:
- CBD/THC goes into effect fast (within 1 hour)
- Higher bioavailability (no first-pass effect)
- CBD/THC benefits last longer than other methods
- Accurate dosing method
Cons of sublingual delivery:
- Can be uncomfortable to avoid swallowing the oil for 60 seconds
- Oil can carry cannabis flavor (terpenes)
- Not as beneficial for targeting a specific area of pain

Now on to edibles. If we’re being smart alecks about it, edibles are really anything you can eat or swallow. But when it comes to CBD and THC, you’ll most likely see them in the form of food (gummies, cookies, brownies) or a pill.
One drawback of consuming CBD and THC via edibles is the decreased bioavailability due to the first pass effect. However, there are ways to increase the reduced bioavailability of consumed CBD and THC.
Foods containing fatty acids and a high lipid (fat) content are perfect pairings for CBD/THC consumption. The cannabinoids bind to these compounds and are metabolized into energy, rather than going through the first-pass effect.
Pros of edible delivery:
- It’s delicious!
- Versatility of using other foods
- Cannabis flavor can be masked
- Discreet way to ingest cannabis
- Long-lasting effects if consumed with food
Cons of edible delivery:
- First-pass effect limits bioavailability
- Harder to dial in dosage
- Not as good for targeting a specific area of pain
Skin (topical creams, lotions, or gels)

The next delivery method for CBD and THC is via topicals. Topicals are any products that can be applied directly onto the skin, including creams, lotions, balms, and salves.
CBD and THC topicals are most often used for pain management and anti-inflammation — both chronic and acute. They are a fantastic way to target isolated muscles and joints for pain relief. Instead of addressing pain at a systemic level, topicals hone in on specific areas for fast relief.
CBD and THC topicals are most often used for pain management and anti-inflammation.
This is a game-changer for folks who deal with chronic joint pain, arthritis, bursitis, fibromyalgia, or pain related to MS. For someone who has been taking 500 milligrams of Tylenol every 4 hours for years, an alternative that doesn’t destroy your liver is a godsend.
One drawback to topicals is that your skin is designed to put up a fight to any foreign substances trying to permeate its walls. In general, the effectiveness of topicals varies greatly depending on the product. They tend to perform best when applied on a local area using a high concentration of CBD or THC.
Pros of topical delivery:
- Targeted pain relief on specific muscles/joints
- Safest approach to consume CBD/THC
- Avoids first-pass effect
Cons of topical delivery:
- It’s hard for CBD/THC to reach the bloodstream
- Not a systemic approach to pain relief
- Need high concentration of product for any effect ($$$)
Lungs (smoking or vaping)

The final method of consuming CBD or THC is to inhale it through your lungs via vaping or smoking. This method yields the fastest and strongest effects. However, it is also one of the more controversial methods because of the potential harmful effects it can have on your lungs.
Vape pens are everywhere these days. In light of the limitations that other methods have because of their decreased bioavailability, vaping is a super viable option. Inhaled as a vapor, the effects of CBD or THC hit your bloodstream almost immediately (usually within 30 seconds). The results, then, are faster and more powerful.
Vaping yields the fastest and strongest effects. However, it is also one of the more controversial methods because of the potential harmful effects it can have on your lungs.
While vaping is a relatively efficient way to ingest CBD and THC, recent reports have shown a dangerous side to vaping. It is still largely unregulated, which means you don’t always know what exactly is in your product. The most dangerous additive to watch out for is propylene glycol, a thinning agent that can be carcinogenic when it is heated up.
Second, while vaping cannabis exposes you to less toxic chemicals than a cigarette, inhaling foreign substances can still by harmful to your lungs. This is especially the case if you vape regularly. Be aware that associated health issues include asthma, coughing, and congestion.
Pros of smoking/vaping delivery:
- Fastest and strongest effect
- Absorbed into bloodstream immediately (side steps first-pass effect)
- Discreet way to consume CBD and THC in public
Cons of smoking/vaping delivery:
- Health concerns associated with vaping/dabbing
- Still unregulated; it’s hard to know exactly what is in your concentrate
- Dosage is hard to control
Legality of CBD vs. THC

While the use of CBD and THC is certainly widespread, the legality of both cannabinoids is still under question. In short, CBD is legal in most cases while THC is illegal. But there’s more to the story.
Remember our earlier definition of hemp? Hemp is any cannabis strain that contains less than 0.3% THC. In the U.S., Congress passed the 2018 Farm Bill, which legalized hemp sales federally. This means that as long as hemp-based CBD remains below the approved THC levels, it is legal in all 50 states.
All around the world, folks are starting to recognize the amazing medical and economic potential of CBD and THC.
The 2018 Farm Bill makes a few qualifications to its legalization of CBD products. Since CBD is still not FDA-approved, it is illegal for companies to sell CBD products with the promise of widespread medical benefits. Even though the medical benefits are anecdotally (and often medically!) proven, the FDA still has not categorically signed off on any claims.
Remember our earlier definition of marijuana? Marijuana is any cannabis strain that contains more than 0.3% THC. While marjiuana use is not federally legalized yet, there are currently 11 U.S. states that have fully legalized the recreational use of marijuana:
- Alaska
- California
- Colorado
- Maine
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Nevada
- Oregon
- Vermont
- Washington
- Washington, DC

An additional 22 states have legalized the use of medical marijuana, which essentially allows you to consume THC as long as you have a prescription from a doctor. You can consult this helpful map of marijuana legality for more state-specific cannabis laws.
When it comes to the legal status of CBD and THC globally, we see some distinct variance. In Europe, most countries have legalized hemp-derived CBD, as long as it stays below 0.2% THC content. In Asia, however, many countries maintain strict laws against cannabis consumption. Latin America has opened the door for a number of laws regarding hemp-derived CBD.
It becomes somewhat more difficult to find countries that have legalized marijuana use, but they certainly exist! Last year, Canada legalized the use of recreational marijuana. Countries like Belize, Jamaica, and Costa Rica have relaxed their laws significantly to decriminalize the use of marijuana, and Mexico is close behind. The country is gearing up to vote on the legalization of recreational marijuana.
Further reading: Check out this fun guide from Thrillist before your next international trip to see if you can light up without looking over your shoulder.
All around the world, folks are starting to recognize the amazing medical and economic potential of CBD and THC. In addition to the U.S., nearly 50 countries around the world have legalized hemp-derived CBD use; others yet are becoming open to the idea of recreational marijuana use. These figures will surely continue to increase as research and policy catches up to public interest.
