CBD. Chances are by now you’ve heard of it. Maybe you’ve even tried it. Maybe your mom has tried it. CBD is suddenly everywhere. And yet most of us are still a little murky on the details surrounding it. Is CBD legal? (Yep). Can CBD get me high? (Nope). Where can I get CBD? (It depends).
Luckily, you’re in the right spot. Welcome to CBD 101. Take a deep breath; we will try to answer all of your questions. Consider this your one-stop guide to the benefits, applications, health regulations, and science behind CBD.
Rise of CBD’s Popularity
In the last few years, CBD has garnered plenty of exciting buzz. And honestly, it’s 100% earned. CBD has shown signs that it might be a sort of “wonder drug.”
Let’s clear up one thing right off the bat. CBD will not get you high. CBD is an abbreviation for cannabidiol. As its name suggests, CBD is a natural compound derived from cannabis. Another natural compound in cannabis is THC or tetrahydrocannabinol (say that three times fast).
However, unlike THC, cannabidiol does not induce psychoactive effects. In fact, it has been suggested that CBD might be able to counteract the psychoactive effects of THC.
Separating CBD from all of the preconceptions about the cannabis plant (marijuana, weed, ganja, kush…you get the drift) is the first step in its resurgence. CBD appears to be safe and (mostly) legal; it has the potential to benefit millions of people with chronic health conditions.

Please be aware that the “Benefits” described in the above chart are not based on any accepted scientific studies but are based primarily on laboratory and pre-clinical studies and testimonials from patients who have used CBD with success.
Health Benefits of CBD
Part of the rapid rise of CBD’s popularity in the United States is due to the huge range of potential health benefits it may provide. Here’s just an initial rundown of some of those benefits:
- May provide pain relief
- May ease anxiety/depression
- May alleviate cancer-related symptoms
- May help provide restful sleep
- May reduce arthritis and joint-related pain
- May reduce acne
- May be beneficial to cardiovascular health
It’s hard not to be a tiny bit skeptical when you look at that list of potential health benefits. It looks to be somewhat overpromising, right? The truth is that in spite of many “claims” about the benefits of CBD there are no substantial scientific studies to validate those claims at present. In this article, we shall examine the most current studies about potential health benefits of CBD and also help you understand the possible mechanisms which underly its potential health benefits.
An excellent 2019 review of the current medical status of CBD was published in the Proceedings of the Mayo Clinic and is an open-access article that can be obtained in its entirety without charge. A recent review in PubMed, the website of the National Library of Medicine turned up 240 new articles published in 2019 about CBD to give you an idea of the medical interest in this intriguing compound.
Endocannabinoid System
To understand the full benefits of CBD, you first need to understand how it interacts with your body. First, let’s take a quick trip through the endocannabinoid system.
The endocannabinoid system (or ECS) is found in lots of different places throughout your body. It is most prominently located in your central and peripheral nervous systems. But researchers have also located receptors in our skin, liver, muscle, heart, gastrointestinal tract, and beyond. So essentially, we’re stocked with this system everywhere.
The ECS is involved in homeostasis. Homeostasis is basically the “checks and balances” of the body to make sure everything is in the right range. The ECS plays a role in important functions like:
- Mood
- Sleep
- Appetite
- Inflammation
- Pain
Here’s how it works. Our bodies naturally produce endocannabinoids. You read that right. We already produce cannabis-like compounds without the help of the plant! The endocannabinoids’ sole purpose is to find their cannabinoid receptor and link up with it. Luckily for us, the ECS has stationed cannabinoid receptors all over our bodies.
When our homeostasis is unbalanced, our body sends out a flood of endocannabinoids. These compounds find their stressed-out cannabinoid receptors in the specific area of the body that is affected. They attach to the receptors like a lock in a key, the cannabinoid receptors breathe a sigh of relief (metaphorically speaking, of course) and homeostasis is achieved!
Then comes the last step of the process. After the job is done, the body sends in enzymes to break up the bonded endocannabinoid and cannabinoid receptor. This prevents any overcorrecting of the process. Remember, homeostasis is all about balance.
Our endocannabinoid system is precise and effective. So why do we need CBD if we already produce our own endocannabinoids? Here are two very simplified answers to that question:
- CBD modifies receptors (cannabis effects without getting us high)
- CBD enhances the natural effectiveness of endocannabinoids
Since CBD is not naturally produced by our bodies, it doesn’t link up directly with the cannabinoid receptor. Instead, it modifies the receptor to remove the potential of the psychoactive THC. It also is known to weaken the receptor that signals for inflammation.
Remember the enzyme clean-up crew? Usually, that process is completely needed for regulation and homeostasis. But CBD is uniquely designed to slow down the enzymes that break down anandamide (a neurotransmitter that seems to affect your mood). In turn, this allows anandamide to stick around in your system longer and potentially improve your mood and reduce anxiety!
Further Reading: A recent study in the British Journal of Pharmacology considers the therapeutic role of cannabinoids (CBD) in easing collateral cancer symptoms, especially as it relates to the endocannabinoid system. The report concludes that “cannabis‐like compounds offer therapeutic potential for the treatment of breast, prostate and bone cancer in patients. Further basic research on anti‐cancer properties of cannabinoids as well as clinical trials of cannabinoid therapeutic efficacy in breast, prostate and bone cancer is therefore warranted.”
What to Look for in CBD Products

Now that we some understanding of the science related to Cannabis and CBD, let’s take a closer look at the product itself. As a general rule, before you ingest something, you want to understand a little more about how it works. Here are some good questions to ask:
- How will it taste?
- How will it make me feel?
- How will it be absorbed into my body?
- How long will it affect my system?
- Will there be any bad side effects?
Well, we’re glad you asked! In this section, we’ll tackle some common words and phrases you might see on a CBD product label. The bottom line is labels are important! They provide helpful answers to the questions above regarding dosage, absorption, flavor, and more. Bear in mind however that because the FDA still considers Cannabis a Schedule 1 Drug there is no standardized testing such as is done with FDA approved drugs and therefore one cannot be sure of the exact representation of components of CBD products available for sale.
CBD Isolate vs. Full Spectrum vs. Broad Spectrum
CBD operates on a spectrum, as does most everything in life. Each product has a varying amount of cannabinoid in it. This all depends on how much cannabinoid is extracted from the cannabis plant in the first place. The process of CO2 extraction is fascinating and complicated.
This is where the cannabis plant meets the science lab. During the extraction process, it is possible to isolate a specific component — even down to a specific cannabinoid — within the cannabis plant. Then, companies can be more exact about the potency, composition, and quality of the product they deliver. Remember though that there is no testing standard for CBD products.
There are three main players in the cannabinoid spectrum: CBD isolate, full-spectrum, and broad-spectrum. Each serves a different purpose and undergoes a different process of extraction and refining. In the end, none of the three are better than the other. Different strokes for different folks! We’ve outlined all three of them below, along with some basic pros and cons of each.
CBD Isolate
As the name implies, CBD isolate is a product that has extracted just CBD from the cannabis plant. Out of all the other possible compounds in the plant, the CBD has been isolated. CBD isolate, then, is the purest form you can find.
Some might assume that the CBD isolate is the most potent since it is in the purest form. However, that distinction is left to full-spectrum CBD.
CBD isolate may be good for people who have a sensitivity to THC or who are trying to avoid it altogether. A CBD isolate will not show up on a standard drug test. Another good aspect of CBD isolate is that it is virtually odorless and tasteless, which is a plus for folks who dislike the “weed” smell.
Pros:
- The purest form of CBD
- Does not contain THC
- No taste or odor
- Does not show up on drug tests
Cons:
- Not as potent as full-spectrum CBD
- The more rigorous distillation process
Full Spectrum CBD
Full-spectrum CBD gets its name for representing the full spectrum of the cannabis plant. In its distillation process, it leaves nothing behind. So in a full spectrum CBD product, you’ll find a range of other cannabinoids, terpenes (more on that in the section below), oils, and other compounds.
This bundle of distilled goodies is a powerful cocktail. In fact, full-spectrum CBD appears to have the strongest results. This is often referred to as the “entourage effect.” Essentially, the entourage effect argues that CBD is most potent in its natural state — with an army of compadre compounds working synergistically.
If you recall the earlier discussion on CBD’s root compounds, you’ll remember that CBD naturally contains THC. THC plays a part in the entourage effect of full-spectrum CBD. Even though the high is canceled out (the cannabinoid receptor has been modified), THC’s presence is crucial in delivering results. That said, however, the amount of THC in a full spectrum CBD extract is tiny; you won’t feel any sort of high. Note also that for a product to be labeled CBD is must contain less than 0.3% THC in the USA or less than 0.1% in the European Union.
Pros:
- Contains full essence of the cannabis plant
- The strongest and most effective form of CBD
- Least amount of processing
Cons:
- Contains tiny amount of THC (not psychoactive though)
- Might show up on a drug test
- Smells/tastes like cannabis
Broad Spectrum CBD
Broad-spectrum CBD is the middle ground between a full spectrum CBD and a CBD isolate. Like full spectrum CBD, a broad- spectrum CBD product brings with it all the extra good stuff in the cannabis plant — terpenes, essential oils, and other cannabinoids. However, like CBD isolate, it does not contain THC.
So broad spectrum still technically enables the “entourage effect” (multiple compounds of the cannabis plant joining forces). But it just doesn’t include the THC. Some would argue that this cancels out the entourage effect, but the jury’s still out.
Broad-spectrum CBD is good for folks who still want a little more “oomph” to their CBD product, but want to avoid THC. For some who live in states in which THC is illegal, broad-spectrum CBD may be a safe, legal choice. In general, broad-spectrum CBD is less available and less popular than its other two siblings. But it works great for some people!
Pros:
- Enables “entourage effect”
- Does not show up on drug tests
- Does not contain THC
Cons:
- Not as well-researched as the others
- Smells/tastes like cannabis
Terpenes

In the discussion about the CBD spectrums, you may have noticed a new word — terpenes. It’s a good word to know; it comes up frequently in CBD products and labels.
The nerdy answer? According to the Oxford Dictionary, terpenes are a group of “volatile unsaturated hydrocarbons that can be found in the essential oils of plants, especially conifers and citrus trees.”
The more palatable answer? Terpenes are an organic compound that affects taste and smell in plants. In the cannabis plant, terpenes are the aromatic compound that accounts for its unique smell. While there is a universal “cannabis smell,” each cannabis plant contains its own unique configuration of terpenes — and therefore each captures its own smell and flavor.
You have maybe experienced this already (or, your nose has). Cannabis embodies its own essence through its array of fragrances — piney, lemony, skunky, fruity, spicy, you name it! The variety of fragrances is due to the differences in terpenes.
Terpenes play a role in CBD beyond just the smell and taste factor. Since terpenes are basically an essential oil, they help in the absorption process of CBD topicals. Terpenes increase skin penetration in topical products.
This dynamic plays into the term we reviewed above — the “entourage effect.” Without the natural oily state of terpenes, we would need a synthetic oil to promote the penetration of CBD into our skin. Terpenes are present in full-spectrum and broad-spectrum CBD, but not CBD isolate.
CBD Dosage

“ CBD might help with my depression, you say? Great! How much should I take?”
That is a very good question! Figuring out an appropriate CBD dosage is crucial to achieving safe and effective results. The only problem is that it is essentially a “trial and error” process.
Part of the issue with CBD dosage is that it is still largely unregulated. That means, among other things, that there are no hard and fast rules to dosage. Dosages anywhere from 20mg to 1,000mg (milligrams) of CBD per day have been suggested. So, where do you fall on that spectrum?
The first and the best thing you can do is talk to your doctor. She or he will likely recommend a dosage that fits your specific needs and lifestyle. Your doctor (and therefore you) will need to consider four essential factors before deciding on a CBD dosage:
- Your body weight / BMI (Body Mass Index)
- Your sensitivity to chemicals
- The condition you intend to treat
- The amount of CBD in your product
- Other prescription or over-the-counter medications that you may already be using.
Some people will absorb CBD faster than others, which may be due to their body weight, BMI, chemical composition, or many other unknown factors. Some people will react better to full-spectrum CBD than CBD isolate. For others, it will be the reverse! As we said before, CBD dosage is a process. Be patient and persistent — you’ll find the right combination!
Here’s a tip: start low on dosage and gradually work your way up or “start low and go slow” as the saying goes. That way, you’ll be able to observe how your body reacts to a range of dosages. For example, you might start at 30mg of CBD per day for a full week. Assess your symptoms. Increase to 40mg if you feel like you need more. It might be a good idea to keep track of your results and track your dosage.
For most CBD products, the label will make it clear how much CBD is concentrated in a serving but beware, you cannot fully trust the labeled amount. This will be simple enough for single-serve products like CBD gummies and capsules. The label might indicate 10mg per gummy, for example.
However, if you are taking CBD oil via a dropper, you’ll want to be more precise. The amount printed on the bottle will usually be the total CBD in the bottle, not the amount of CBD in a single drop. You will need to do some calculating to determine the amount of CBD in a single drop. Here is an example of how such a calculation might be done:
- Total CBD in 5-mL bottle: 1,000mg
- 1 drop = 0.05 mL (100 drops in the bottle)
- 1000mg / 100 drops = 10mg per drop
All in all, when it comes to CBD dosage, just take your time, read the label, and start your dosage low. The great thing about CBD is that it is difficult to overdo it, but side effects and toxicity of CBD have been reported!
Methods of Taking CBD
One highly marketable aspect of CBD is its ability to “shapeshift” into numerous forms for intake. For example, these methods include gummies, drops, capsules, topicals, teas, and other drinks and more. This shape-shifting happens at the production stage. CBD manufacturers are asking: What are the easiest, most efficient ways to take CBD?
Here’s what they have come up with! At this point, the three most popular methods of taking CBD are orally, topically, or inhaling through vaping. Another way to put that — you can ingest CBD through your mouth, skin, or lungs.
There are pros and cons to all of the methods. Each serves a specific purpose, too. We’ve laid them out below for you to decide what fits best with your needs!
Orally

The first method of taking CBD is orally, or through your mouth. This is probably the method that most people associate with taking a pill. And therefore, oral ingestion of CBD tends to still be the most popular method.
Oral intake of CBD is most effective for people who want a systematic approach to their symptoms. Usually, folks find that oral intake of CBD scores big in the following: it is more exact in dosing, faster in implementing effects, and achieves results that last longer. Within this category, you’ll find the sublingual (under the tongue) and buccal (lining of the mouth) CBD methods, as well as the edible CBD method.
Sublingual / Buccal
Sublingual technically means “situated or placed under the tongue.” So, to ingest CBD sublingually, it means you will place a few drops of a CBD tincture or oil under your tongue. It is recommended that you hold it there for at least 60 to 90 seconds before swallowing.
Here’s why the sublingual method works so effectively. Underneath the tongue is a bed of capillary-rich tissue. By placing the CBD directly on this tissue, you are essentially delivering the goods directly to your bloodstream. You will usually feel the effects within 1 hour.
In fact, the sublingual method totally side-steps the first-pass metabolism process that happens when a substance goes through your digestive tract (if you were to ingest it like food). This metabolism process can delay the effects of CBD and lessen its potency. It can take up to 2 hours to feel the effects of CBD that is eaten.
Another approach is the buccal method. Buccal is another fancy anatomical name for “cheek.” In this method, you would drop a dosage of CBD oil against the inside of your cheek and hold it there for 60 to 90 seconds. The lining of the cheek is also rich in capillaries resulting in good absorption of CBD. The sublingual method tends to be more effective than the buccal method, but both work well.
We’re discussing a term here known as “bioavailability.” Basically, it’s how much of a substance is available to your body after you ingest it.
For example, to get 100% bioavailability, you would need to administer CBD intravenously (directly into your bloodstream). Since the sublingual or buccal methods route the CBD almost immediately into your bloodstream, they provide higher bioavailability than swallowing a CBD capsule.
Pro Tip: If you swish the CBD oil around your mouth and teeth during that 90-second window, you’ll boost the effects even more. This maximizes the surface area that can absorb the CBD into your bloodstream.

If you forget to hold the oil under your tongue, or if you accidentally swallow it immediately, don’t worry about it. You’ll still get the CBD dosage — it just might take longer for you to feel the effects.
The sublingual and buccal method is best used with CBD oils or tinctures. You might not be familiar with the word “tincture.” A tincture is a medicine (or CBD) that has been infused with another solvent, usually alcohol or oil.
CBD tinctures differ from CBD oils in that they are infused (rather than in its purest form) with other substances, usually alcohol. Other ingredients — like terpenes, other carrier oils, etc. — can be added to tinctures, too.
You can buy CBD tinctures as well as CBD oil. When you’re using a CBD tincture, just remember our recommendations about dosage. Start small (at around 20mg of CBD) and build up slowly according to your symptoms. CBD tinctures can really pack a punch. You don’t need much to feel the effects.
One big benefit of using a CBD tincture or oil is that you can control your dosage better than a pre-dosed capsule or edible. As you consider whether the sublingual and buccal method is best for you, here’s a round-up of the benefits of this method:
Pros of Sublingual / Buccal Method:
- CBD goes into effect fast (within 1 hour)
- Higher bioavailability
- CBD effects last longer than vaping
- Tinctures have a long shelf life
- Droppers are an accurate way to dose CBD
Cons of Sublingual / Buccal Method:
- Some people don’t like holding oil in their mouth for so long
- Oil can carry cannabis flavor (terpenes)
- Not as good for targeting a specific area of pain
Edibles
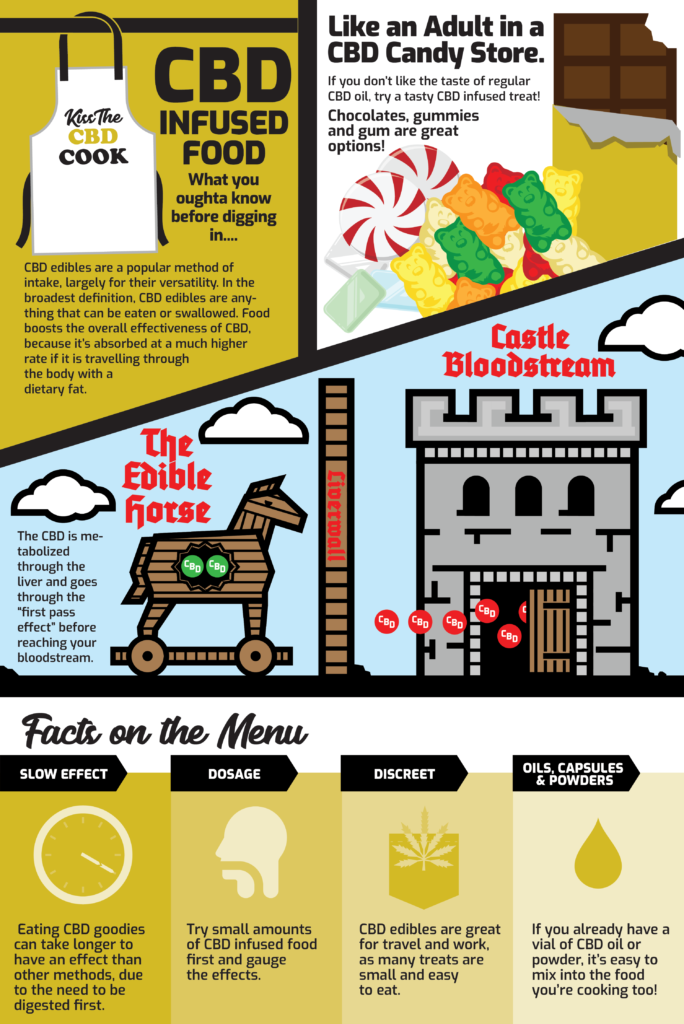
The second category within the oral intake of CBD is edibles! CBD edibles are a popular method of intake, largely for their versatility. As a classification, edibles are probably more than what you’re picturing (gummies, brownies, etc.). In its broadest definition, CBD edibles are anything that can be eaten or swallowed.
CBD edibles can take numerous forms. They could be pills, capsules, powder, or oils that you mix into food or drink.
The most popular form of edibles is CBD-infused food. There are so many products out there that are infused with CBD — gummies, chocolates, mints, truffles, gum…the list goes on and on. Part of the draw is that we love these foods on their own. The addition of CBD is just a bonus!
But there is another more practical reason CBD pairs well with food. Food, particularly fatty food may boost the overall effectiveness of CBD. CBD is fat-soluble. This means that the body will absorb your CBD dosage at a much higher rate if it is traveling through the body with dietary fat.
Further Reading: This 2016 study from the American Journal of Translational Research takes a look at how dietary fats and pharmaceutical fats can boost your body’s exposure to cannabis. This study cautions that taking CBD with food may cause an “overdose” with unpleasant side effects or toxicity. One drawback of consuming CBD via edibles is its decreased bioavailability due to the “first-pass effect.” When we consume CBD orally, it travels through our digestive tract and eventually makes its way to our intestines. There, the CBD is absorbed into our bloodstream and passes through the liver (via the hepatic portal system, if you want to get exact).

The liver functions to process and metabolize substances from the digestive tract. This is the “so-called” “first-pass effect.” In this process the liver uses enzymes to break down the CBD. This dramatically reduces the biological availability of CBD and therefore the effect of any one dose. In fact, most of the CBD end up being excreted via urine.
There are ways to increase the reduced bioavailability of consumed CBD. As was explained above, foods that contain fatty acids and high lipid (fat) content may be good to pair with CBD. Examples of such foods are:
- Coconut oil
- Avocado
- Eggs
- Nuts
- Coffee with cream
Further Reading: A 2012 study from the European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology shows that the bioavailability of CBD is 3 to 5 times higher if it is consumed with food and as mentioned, the biological effect may be greater than anticipated, leading to unpleasant side effects or even toxic effects.
Dosage for CBD edibles is somewhat trickier than it is for the sublingual and buccal methods. The combination of a CBD edible with food introduces other factors that may affect how the body will absorb and process the CBD. In turn, this makes it harder to get dosing precise. As always, take the time to read labels and start slow!
Pros of Edibles:
- Delicious!
- The versatility of using other foods
- Cannabis flavor can be masked
- A discreet way to ingest CBD
- Long-lasting effects if consumed with food
Cons of Edibles:
- First-pass effect limits bioavailability
- Harder to dial in dosage
- Not as good for targeting a specific area of pain
Topicals

The next method of using CBD is via topicals. Topicals are a medication (in this case, CBD) that can be applied directly to the skin. This could include creams, lotions, balms, salves, or anything else in that category.
CBD topicals show great promise as anti-inflammatory agents to provide relief from joint and muscle pain. You might use CBD topicals for acute and chronic pain. Instead of offering a systemic approach, topicals target specific areas that are causing pain. Topicals perform best when applied to a local area using a high concentration CBD product.
Further Reading: A study published in Molecules last year (2018) explores the beneficial effects (and the variety of delivery methods) of CBD as it addresses chronic pain and inflammation. The article also includes this cautionary note: “Cannabis-derivative-based medicines may be able to enrich the drug treatment arsenal for chronic pain and inflammation conditions, although this is very much open to debate at the moment.”
While topicals can get very specific in location, they sometimes lag in precision when it comes to timing. In general, the effectiveness of topicals varies greatly depending on the location. Unfortunately, intact skin does not have great permeability. Permeability is the level to which substances can pass through a membrane.
One way to increase permeability is to find a topical that includes terpenes (so a full- or broad-spectrum CBD topical). The essential oils in terpenes naturally boost skin penetration. Another great option is to pair a CBD topical with a systemic CBD product. In that way, you may possibly increase your pain relief to an isolated muscle or joint, while still experiencing systemic benefits. A recent study concluded that enhancers do increase the bioavailability of trans-dermally applied CBD.
While the skin does not have great permeability, areas with mucous membranes do. They lack the dermal “defense layers” of our skin. Mucous membranes are usually found in our internal organs. However, one area in which skin is continuous with a mucous membrane is our genital areas.

In fact, CBD has been considered as an approach to a number of gynecological issues, such as:
- Severe menstrual cramps
- Pain during sex
- Pregnancy nausea
- Painful urination
- Hemorrhoids
CBD topicals aren’t just for addressing pain. CBD lubrication is becoming increasingly popular for its benefits in the bedroom. It has been said to reduce pain and anxiety during sex, and even act as a natural aphrodisiac. Genital topicals can be found as lube, creams, sprays, or suppositories.
In areas that where there is no mucous membrane, the best chances option for an effective topical may be a CBD patch. Unlike a cream or lotion, CBD patches are transdermal. This means they are “pre-loaded” with a dose of CBD and have the ability to cross over the skin (dermal) barrier.
Further Reading: This 2015 study demonstrates (using rats!) that transdermal application of CBD reduces pain and inflammation symptoms of arthritis. As previously mentioned, however, the safety and effectiveness of Cannabis in the treatment of pain and inflammation are: “very much open to debate at the moment.”
Even though it is harder to find a topical that is 100% effective, CBD topicals hold promise for many people with chronic health issues.
Those who suffer from arthritis or bursitis (or other joint pain conditions) can potentially benefit from topicals. Topicals may also be effective at the muscular level. People who deal with chronic back pain or fibromyalgia may be improved with CBD topicals.
Further Reading: In early October 2019, the Arthritis Foundation released a set of guidelines instructing patients on how to use CBD to manage arthritis-related pain. The guidelines stress that there have been no rigorous clinical studies to prove the benefits of CBD in treating the symptoms of Arthritis.
Allied health professionals are also beginning to employ CBD products. With the appropriate waivers and legal parameters, massage therapists, physical therapists, chiropractors, and acupuncturists are beginning to incorporate topicals into their sessions. Another potential market for topicals is in the sports arena for athletes who are seeking targeted pain relief.
Pros for Topicals:
- Topicals target specific, localized areas for pain relief
- The safest approach to consuming CBD
- Avoids the first-pass effect
- Highly effective on mucous membranes (genitals)
- Transdermal patches permeate the skin barrier
Cons for Topicals:
- Skin offers poor permeability (hard for CBD to reach the bloodstream)
- Not a systemic approach to pain relief
- Need a high concentration of CBD for any effect (can be expensive)
Vaping

The final method of taking CBD is vaping or inhaling it. This is the method that yields the fastest and strongest effects of CBD. However, it is also one of the more controversial methods because of the potentially harmful effects it can have on your lungs. Vaping has been recently declared illegal in certain localities so you should consider carefully the potential health risks as well as the particular legal situation in your community before considering vaping CBD.
A recent article in the New York Times indicated that a substance called Vitamin D Acetate may be responsible for vaping related lung disease. Vitamin D Acetate is a gummy substance which can be added to vaping devices by the manufacturers to dilute THC or nicotine. At present, the United States Centers for Disease Control (CDC) recommends against vaping any substance. The lung disease associated with vaping has been compared to the “lung burns” suffered in World War I due to Mustard Gas and have left those affected in hospitals and often in intensive care units. Over 2000 cases of vaping-related lung disease have now been reported.
Vape pens are ubiquitous these days and you should definitely avoid using those obtained from illegal sources. Their rise in popularity is in part due to their branded status as a healthier counterpart to smoking although that is an uproven contention. As opposed to smoking, vaping is a potentially less toxic process. It occurs at a lower temperature, activates vapor (rather than smoke), and may not contain as many carcinogens.
In light of the limitations that other methods have because of their decreased bioavailability, vaping may be a viable option. Inhaled as a vapor, the effects of CBD enter the bloodstream almost immediately (usually within 30 seconds). The results, then, are faster and more powerful.
Let’s back up for a second. Maybe vaping is new to you. If so, vaping is a method of inhaling CBD (and other substances). Vaping requires a device that heats up to vaporize a substance, which you subsequently inhale.
When it comes to inhaling CBD, you’ve got three main hardware options:
- Vape pens
- Wax pens
- Dab pens
We’ll go into much more detail about these devices below. But as you sort through these three methods, here are some key factors to consider:
- What is the vaping technique?
- What is the hardware that is required?
- How does the quality compare?
- How much does it cost?
Vape Pens
Vape pens are probably the device that you are the most familiar with and have seen people use. They contain a cartridge that holds the CBD oil or liquid. When you inhale, an atomizer inside the pen will heat the CBD oil, turning it to vapor. Vape pens are battery-operated, usually rechargeable, and discrete. They fit easily into a pocket or purse.
Wax Pens
Wax pens are similar to vape pens in their hardware structure. However, instead of oil or liquid in the cartridge, wax pens literally meltdown a CBD wax concentrate. Since they are dealing with a more solid substance, wax pens require higher heat.
Dab Pens
Dab pens are a more specialized device — they only work with dab concentrates. What is a “dab”? A dab is a highly concentrated extract of CBD that gets flash heated in the dab pen. The dab turns into a liquid, which in turn gets vaporized when inhaled. Wax and dab pens sometimes considered interchangeable. However, even though they both deal with concentrates, they require separate substances.
Overall, the three techniques share many similarities, mostly in their hardware. However, here are some key differences to consider:
- Dab pens are more potent in CBD content than vape pens
- Dab and wax pens can be messier to load than vape pens
- Dab pens use a much higher temperature than vape pens
While vaping is a relatively fast and effective way to ingest CBD, recent reports have revealed a more dangerous side to vaping. First, vaping and e-cigarettes are still largely unregulated. This means you need to be extra careful about where you source your vape liquid, oil, waxes, and dabs. Some companies use flavoring and additives that prove to be carcinogenic and toxic.
Second, while vaping cannabis exposes you to less toxic chemicals than a cigarette, inhaling foreign substances can still b harmful to your lungs. This is especially the case when if you are regularly vaping.
Some associated health issues include:
- Chronic cough
- Congestion
- Asthma
Since CBD liquid can be an expensive product, some distributors have been known to add propylene glycol to the concentrates. Propylene glycol is a thinning agent that can be carcinogenic when it is heated up. Bottom line, know exactly what is in your CBD product before inhaling it!
Further Reading: A 2017 study in Psychological Reports shows that one side effect of e-cigarette vapors is a gene modification of your circadian rhythm — therefore altering core biological expressions. According to the study, this is largely due to exposure to propylene glycol.
Pros of Vaping CBD:
- The fastest and strongest effect
- Absorbed into the bloodstream immediately (side-steps first-pass effect)
- A potentially less toxic counterpart to smoking
- Discrete way to consume CBD in public
Cons of Vaping CBD:
- Health concerns associated with vaping / dabbing
- Still unregulated; hard to know exactly what is in your concentrate
- Dosage hard to control
- Potentially serious side effects and toxicity especially to the lungs.
CBD and Regulation

Despite the relative widespread access to CBD nationwide, regulation and legality are still somewhat unclear. Policy is still catching up to public interest. In July 2019, the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) released their take on the science and safety of CBD products. The current status of CBD at the federal level is complicated. We’ve done our best to spell out some of the big questions below.
Is CBD Legal?
The big question everyone is wondering: Is CBD legal? The short answer is yes! But the longer answer is a bit more complicated.
On the federal level, purchasing CBD is legal as long as the strain contains less than 0.3% THC. In the 2018 Farm Bill, Congress legalized hemp sales federally. The hemp plant is in the cannabis family. If hemp contains more than 0.3% THC, however, it is considered marijuana, which is still illegal on the federal level.

There are currently 11 U.S. states that have legalized the use of marijuana: Alaska, California, Colorado, Maine, Massachusetts, Michigan, Nevada, Oregon, Vermont, Washington, and Washington, DC. An additional 22 states have legalized the use of medical marijuana, which essentially allows marijuana as long as you have a prescription from a doctor.
When it comes to the legal status of CBD worldwide, it varies somewhat. In Europe, most countries have legalized hemp-derived CBD, as long as it stays below 0.2% THC content. In Asia, however, many countries maintain strict laws against cannabis consumption. Latin America has opened the door for a number of laws regarding hemp-derived CBD. An excellent review of the legal status in many countries of the world can be found here. Mexico is now voting on the legalization of recreational marijuana. Across the globe, both the public and policymakers are gaining interest in the positive potential of CBD. Already, nearly 50 countries around the world have legalized hemp-derived CBD use. That number will continue to grow as science and research catch up to public interest.
Is CBD Well-Researched?

Part of the difficulty in legitimizing and legalizing cannabis products on a federal level is the relative lack of clinical research to back up claims about CBD. Until the FDA backs CBD as a whole, the research will be under-funded and less accepted in the medical community.
Further Reading: This 2017 article explores the various regulatory and financial barriers that face the cannabis industry, especially as it relates to conducting ongoing research.
That is not to say there is a total lack of studies out there on CBD. In fact, we have included references to or discussion of some of the available studies throughout this guide that are backed by clinical trials and published in peer-reviewed medical journals. Articles about CBD in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders, anxiety-related and substance abuse disorders, inflammation, panic attacks, inflammatory bowel disease, as a potential anti-cancer drug, for neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. A well- designed placebo-controlled, double-blind study of CBD to treat Schizophrenia which appeared in the 2018 American Journal of Psychiatry concluded that “CBD has beneficial effects in patients with schizophrenia. As CBD’s effects do not appear to depend on dopamine receptor antagonism, this agent may represent a new class of treatment for the disorder.” Several recent review articles of many aspects of the therapeutic potential of CBC can be found here and here and here and here. As a whole, though, CBD research is still in its early stages and the vast majority of studies recommend that large, well-controlled, human studies of CBD should be carried out. One of the major problems with many studies of CBD is that they employ different dosages under different conditions which makes comparing different studies difficult or impossible. But whatever the deficiencies in CBD studies it is very clear that there is much more to learn about this amazing plant!
Are There Side Effects to CBD?

If you are considering using CBD for the first time, the best thing you can do is talk to your doctor. Your doctor will be able to give you a recommendation for dosage, method, and use according to your specific health needs.
While the side effects of CBD are relatively mild, there are a few precautions to consider. In some rare cases, CBD side effects have included:
- Somnolence
- Diarrhea
- Weight change or appetite change
- Fatigue
- Anxiety
Another precaution to take before using CBD for the first time is to review your current medications with your doctor. Your doctor will be helpful in advising which prescription medications could possibly mix poorly with CBD.
Maybe you’ve heard of the “grapefruit rule.” Doctors warn against mixing some medications with grapefruit juice. Common ones are Lipitor (cholesterol medication) and Claritin (allergy medication). Grapefruit juice interferes with enzymes in your liver, which in turn affects how you metabolize the medication.
If you are on these medications, it can be dangerous to add CBD to the mix. CBD acts in a similar way to grapefruit juice by inhibiting the enzymes that metabolize your medication. As a result, your medication can stay in your system longer. As a rule, just make sure your doctor signs off on your CBD usage.
The Bottom Line
Hopefully, by now it’s clear to you that CBD is a wildly useful and versatile product that can yield huge health benefits. If you are new to CBD, you have lots of different options in using it for the first time: consuming it orally, topically, or inhaling it. You may be able to use CBD to treat chronic health conditions, anxiety, sexual health, and more but I thorough discussion with your doctor is essential before you begin to treat yourself with CBD. Hemp-derived CBD products are legal in the United States, as long as they contain less than 0.3% THC. Similar laws are in place in over 45 different countries.

Beyond ingesting CBD to address health concerns, you can find CBD in tons of other fun day-to-day products like makeup, soaps, shampoos, and bath bombs. Even more, CBD is not just beneficial to us. CBD is also a useful for our best friends — our pets! You can find CBD pet treats and tinctures to treat pet anxiety, joint pain, and more. We suggest that you discuss your pet’s medical situation with your veterinarian before beginning a course of treatment with CBD.
Our understanding of CBD is continually expanding, especially as clinical research in the area picks up speed. But what is the bottom line? CBD is relatively safe and studies, such as they are, suggest that CBD may be effective in treating a variety of medical conditions. Further clinical studies are needed to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of CBD. Our bodies are literally designed to interact with its healing properties. Now that you’re practically an expert in CBD, you may consider giving it a try yourself!
